Snippets
- Understanding renewable energy integration into power grids.
- Identifying challenges like variability, grid stability, and storage limitations.
- Practical solutions to enhance renewable energy reliability.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Renewable energy is undeniably the cornerstone of a sustainable future, but integrating it into existing power systems is far from simple. While solar and wind power shine as clean alternatives, they bring along challenges like variability, grid imbalances, and limitations in energy storage. Did you know that in some regions, renewable power curtailment reaches 30% due to grid congestion? Let’s uncover the key hurdles in renewable energy integration and, most importantly, practical solutions to address them effectively.
The Variability of Renewable Energy Sources
One of the most significant hurdles in renewable energy integration is variability. Unlike conventional power plants, which provide consistent energy, renewable energy sources like solar and wind depend heavily on weather conditions. This unpredictability creates power fluctuations that strain existing grid systems.
For instance, during overcast days or windless periods, energy production dips dramatically, making it difficult to ensure a stable power supply. Conversely, when production exceeds demand, excess energy must be curtailed to prevent grid overload, resulting in wasted resources.
To address variability, energy forecasts play a crucial role. Advanced weather prediction models combined with AI-driven analytics can help operators anticipate production changes. Moreover, a diversified energy mix — combining solar, wind, and other renewables like hydropower — can smooth out inconsistencies. By strategically positioning renewable installations across various regions, it’s possible to balance energy fluctuations and enhance reliability.
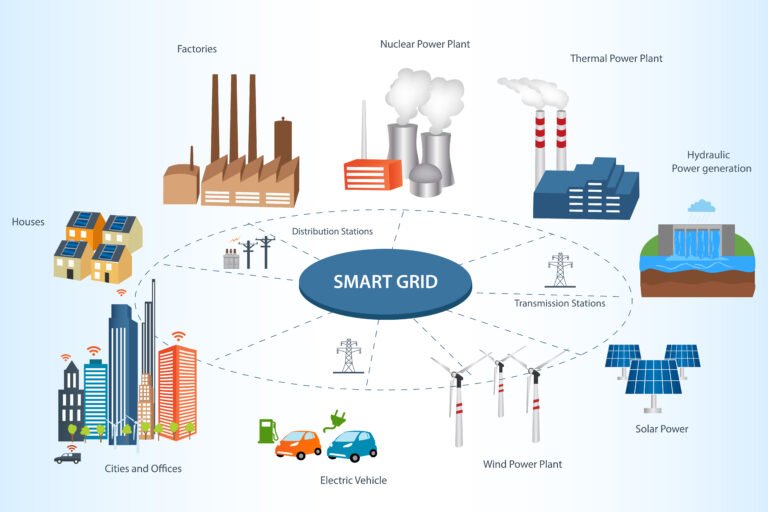
Grid Stability and Balancing Issues
Traditional power grids were designed for consistent, centralized energy generation. Integrating renewables disrupts this model because energy production from solar and wind is decentralized and intermittent. This imbalance affects grid stability, making power management a challenge.
Take California, for example. The state has invested heavily in solar energy but faces significant grid challenges during peak generation hours. When solar panels produce an abundance of energy in the middle of the day, grids experience overload, leading to curtailment or, worse, power outages.
To improve grid stability, smart grids and digital solutions are essential. Smart grids use advanced communication and control systems to monitor energy flow in real time, enabling operators to adjust supply and demand dynamically. Additionally, flexible demand-response programs allow industries and consumers to shift their energy usage to off-peak hours, improving load balancing.

Stay Informed. Stay Ahead
Join a community that goes beyond the headlines. Our newsletter delivers:
🔹 Curated Industry Insights
🔹 Expert Analysis
🔹 Actionable Impact
No fluff. No generic updates. Just meaningful insights that help you lead in a fast-evolving industry.
Energy Storage Limitations
Energy storage is the key to solving variability and grid stability issues, but current storage technologies face critical challenges. Batteries, for instance, are expensive and have limited scalability. While lithium-ion batteries dominate the market, their production involves high costs and environmental concerns, restricting widespread adoption.
Grid-scale storage systems like pumped hydro storage or emerging technologies such as hydrogen-based storage offer promising solutions. For example, hydrogen can store surplus energy produced by renewables and release it later when demand spikes.
The solution lies in investing in innovation. Breakthroughs in battery chemistries, such as solid-state batteries, are reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Governments and private sectors must collaborate to expand energy storage infrastructure, ensuring renewables can be reliably stored and deployed when needed.
Infrastructure and Transmission Bottlenecks
Current power transmission infrastructure is inadequate to handle the decentralized nature of renewable energy. In many regions, energy generated from solar farms and wind turbines cannot reach consumers due to outdated grid systems. This leads to transmission bottlenecks and curtailment of valuable renewable power.
Countries like Germany have recognized this issue and are upgrading their power grids to accommodate renewable energy flows. Germany’s “Energiewende” policy focuses on expanding high-voltage transmission lines and deploying flexible grid technology.
The solution involves modernizing infrastructure by investing in robust, high-voltage direct current (HVDC) lines, which efficiently transport energy across long distances. Upgrading grid capacity and integrating microgrids at a local level will also help accommodate renewables while ensuring minimal energy loss.
Policy and Economic Barriers
Government policies and economic challenges often hinder renewable energy integration. High upfront costs of renewable projects and storage systems deter investment, while policy frameworks in many regions are outdated or non-supportive of clean energy adoption.
However, successful models exist. Countries like Denmark and Spain have implemented feed-in tariffs and tax incentives to encourage renewable energy projects. By providing subsidies, governments can offset installation costs, making renewables competitive with fossil fuels.
Policymakers need to prioritize supportive frameworks, such as carbon pricing mechanisms and clean energy mandates. Promoting public-private partnerships will further drive innovation and accelerate grid modernization projects, ensuring a smooth transition to renewable energy.
Conclusion
Integrating renewable energy into power grids is a complex but crucial endeavor for a cleaner future. From tackling variability to enhancing storage and upgrading infrastructure, solutions exist to overcome these challenges. Policymakers, engineers, and innovators must collaborate to ensure renewable energy fulfills its potential. With the right technologies and policies in place, we can pave the way for a resilient, sustainable energy system. Let’s work together to embrace clean power and secure a brighter future for generations to come!







Great breakdown of poker strategies-really appreciate the analytical depth. It reminds me of the blend of luck and skill in SuperPH, especially with its wilds and free spins feature. Both demand smart play!
That analysis is spot on! Seeing platforms like philwin ph really understand the local gaming scene with options like GCash is awesome. It’s about more than just games, it’s the experience! Hoping to see more localized options in esports betting soon too. 🔥
Smart bankroll management is key with online gaming! Seeing platforms like UBet95 integrate quick deposits (even 100 PHP!) & secure fintech is reassuring. Explore ubet95 slot options responsibly, and always set limits. It’s about entertainment, not income!